Coconut Oil
[Raw Material] - Coconuts
[Finished Product] - Detergents, Soaps, Whipped cream, Ice cream, Coconut oil
Coconut oil is an edible oil that is extracted from the coconut which grows from a tall tree named coconut palm.
Coconut oil is difficult to oxidize and it contains more than 90% of stabilized saturated fatty acid.
It also contains medium chain fatty acid so it is said to have effects on the diet, lowering cholesterol value, improving immunity and re-energizing the brain.
About 60% of coconut oil is used as industrial raw materials for items such as detergent and soaps. The other 40% is for edible use.
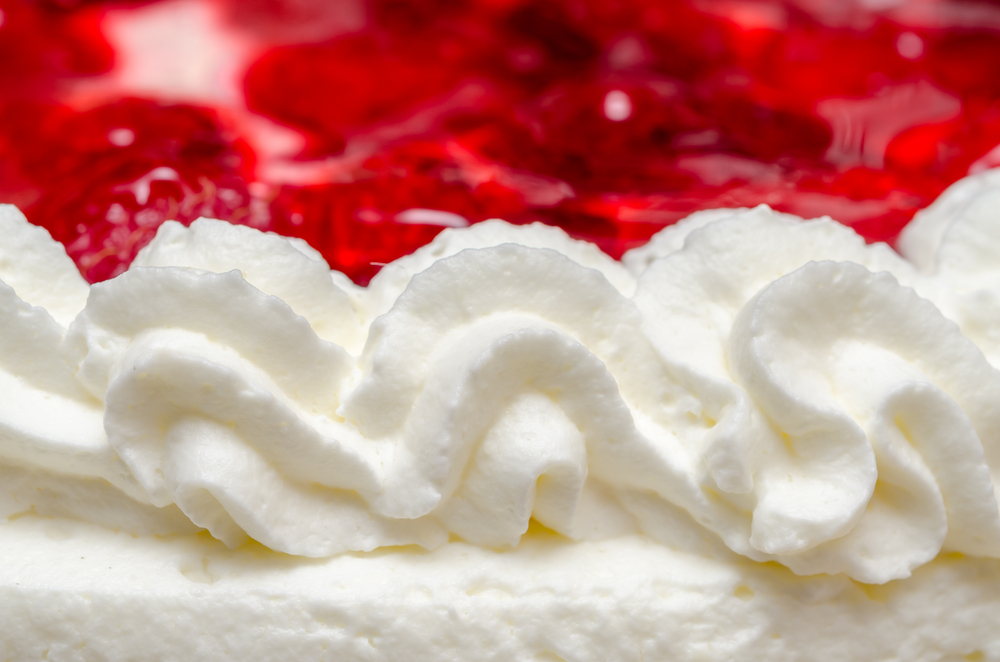
By hydrogenating coconut oil, it can also be used as a substitute product for cocoa butter. Since its characteristics are close to those of milkfat, it is used as a raw material for whipped cream, coffee cream and ice cream.
Due to the high medium chain fatty acid rate, coconut oil is easy to digest and metabolize so it also used for food prepared for infants and patients.
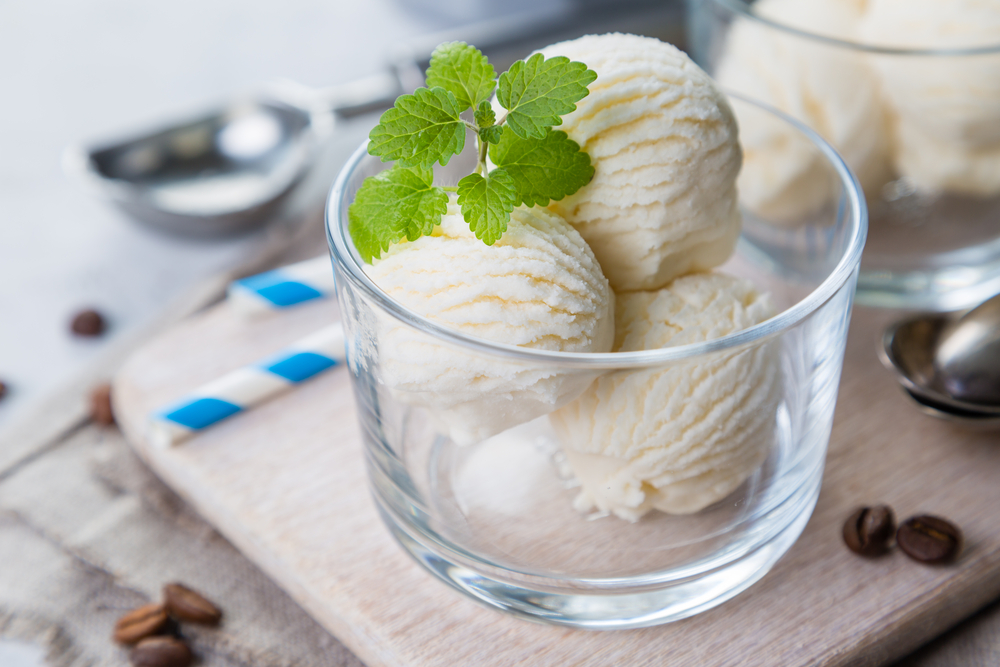


Coconut oil is refined using two major ways. Chemical refining and Organic refining.
Chemical refining is an economical way of refining that creates coconut oil by using chemical.
Chemical refining involves the removal of free fatty acids and other impurities by means chemical agents.
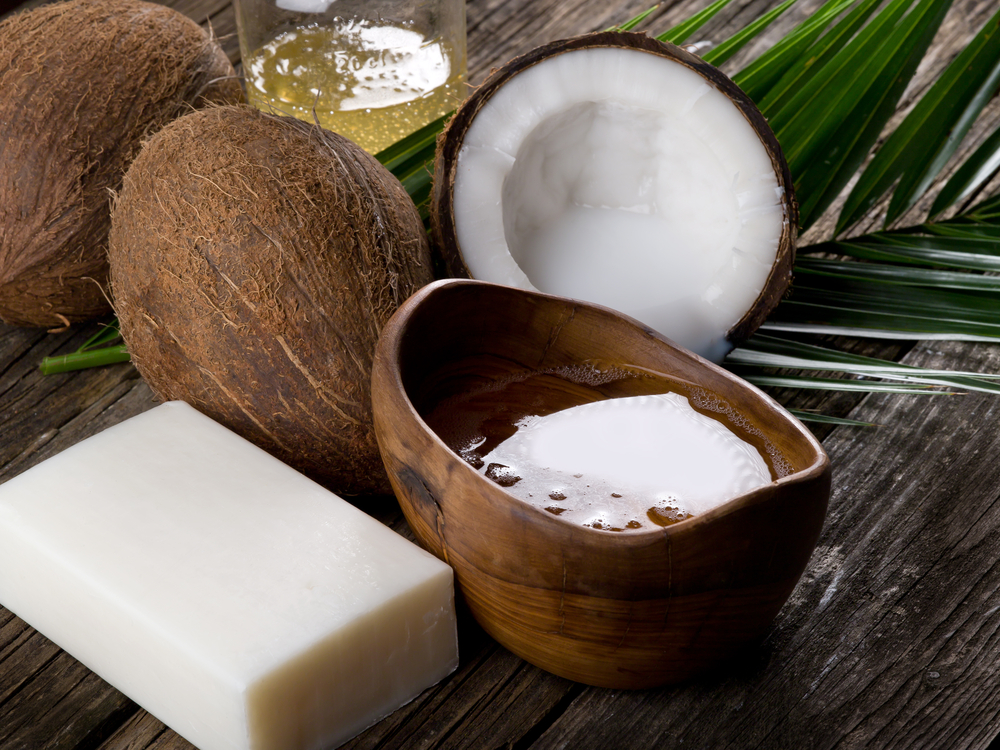
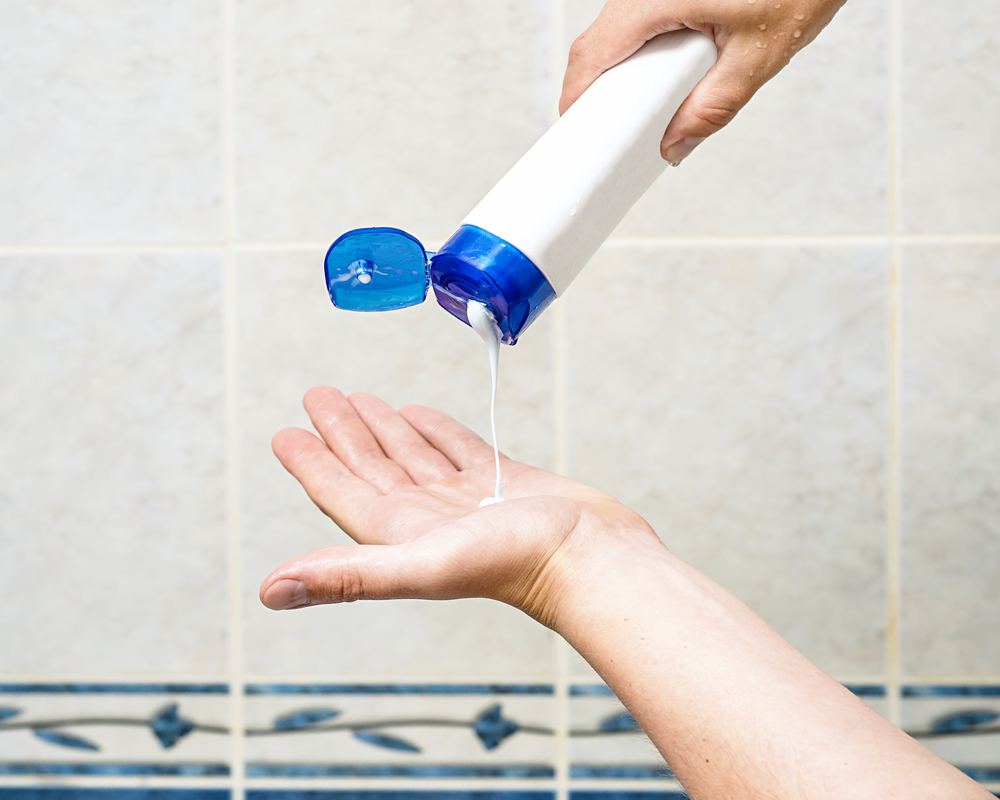


Coconut oil created by using organic refining is also called virgin coconut oil.
It is pressed at a low temperature and extracted.
Since it is a made in a more natural way, it is difficult to maintain freshness and it takes time and effort to produce the oil in large quantities.
However, the oil refined by this organic refining maintains enzymes and rich minerals that are good for your body.
That is the reason why this oil is popular and expensive and used for beauty products such as body creams, massage oils, cleansing products and face care.


Organic Chemical
-
Aromatics
-
Monomer
-
Others
Vegetable Oil
Others
-
Inorganic Chemical
-
Others


 Company Profile
Company Profile Statement
Statement History
History Access
Access Work for Safety
Work for Safety Work for the Environment
Work for the Environment Intra South East Asia Trade
Intra South East Asia Trade Our Chemical Tankers
Our Chemical Tankers About Our Cargoes
About Our Cargoes Fleet List
Fleet List